Bottled Brilliance – Collecting and Enjoying Limited Edition Whiskeys
In the realm of spirits, few elixirs embody the essence of craftsmanship, history and sophistication as exquisitely as limited edition whiskeys. These elusive bottles are not mere libations; they represent an amalgamation of time, skill and the artistry of master blenders. To collectors and enthusiasts, each bottle is a narrative, a piece of liquid history encapsulated within its glass confines. The allure of limited edition whiskeys lies not only in their rich flavors but also in their scarcity. These spirits are often the result of meticulous processes, refined over decades, embodying the legacy of their distilleries. Whether it is a small-batch release, a single cask offering or a special edition celebrating a milestone, each bottle signifies an intersection of tradition and innovation.
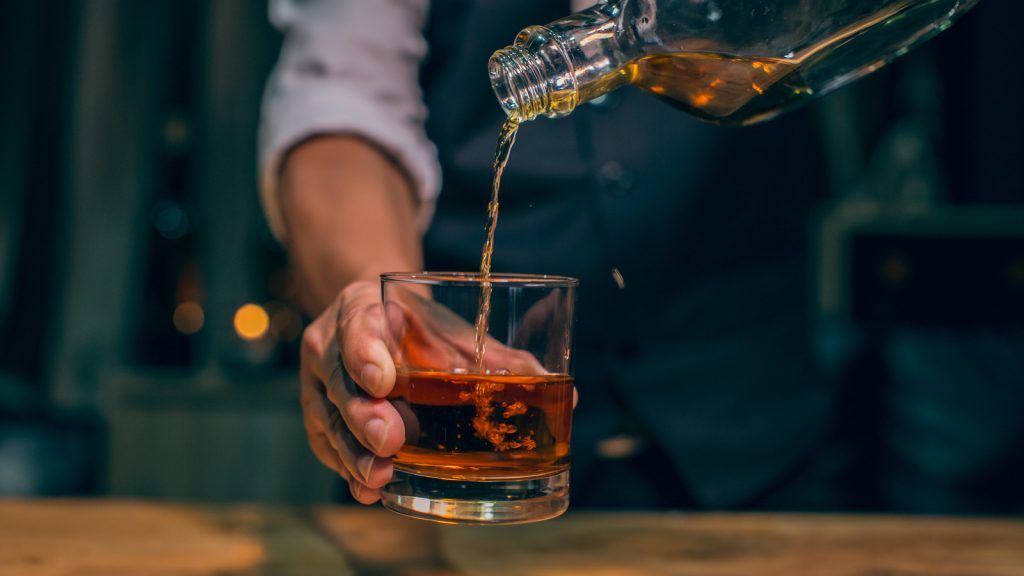

Collectors view these whiskeys as more than a drink; they are an investment in a liquid legacy. The exclusivity of these bottles gives rise to a thriving market where aficionados and investors alike seek to acquire these treasures. The rarity, coupled with unique packaging and the story behind the creation, adds to the appeal and desirability of these limited editions. For connoisseurs, collecting these whiskeys becomes an adventure, a pursuit to own a piece of liquid history. The appreciation of limited edition whiskeys extends beyond their monetary value. Tasting these exclusive spirits is an experience steeped in ritual and reverence. The opening of a bottle marks the commencement of a sensory journey. With each pour, one discovers a symphony of flavors, meticulously crafted notes that dance on the palate, revealing layers of complexity and depth unique to these limited releases. Some are reminiscent of aged oak and peat, while others boast hints of caramel, vanilla or spices. Each sip tells a story, leaving a lasting impression on the discerning drinker.
Moreover, the community surrounding limited edition whiskey is as diverse as the spirits themselves. Tastings, auctions and gatherings become platforms for enthusiasts to share their knowledge, experiences and, at times, their prized possessions. The camaraderie among collectors fosters an environment where stories are exchanged and knowledge is passed down, enriching the collective understanding of these liquid treasures and has a peek here https://theboozeshelf.com/article/what-is-whiskey-everything-about-bourbon/. However, the pursuit of these exceptional spirits demands patience, dedication and a keen eye. The quest for rare bottles might take collectors to auctions, specialized retailers or even directly to the distilleries. Sometimes, it is the thrill of the chase that makes the reward even sweeter. In conclusion, the world of limited edition whiskeys is a tapestry woven from tradition, innovation and exclusivity. Collectors and enthusiasts savor not just the liquid in the bottle but the heritage, craftsmanship and stories each unique release encapsulates. The allure of these bottles lies in their scarcity, their intricate flavors and the sense of community they foster among those who seek to explore and relish the finest in whiskey craftsmanship.



 In contrast, industrial coffee tables have gained popularity for their rugged and utilitarian charm. Made from materials like steel, concrete, and reclaimed wood as coffee table manufacturers, these tables exude a raw, unfinished look. Industrial coffee tables often feature sturdy construction and distinctive features such as wheels, gears, or visible hardware, making them ideal for adding an urban, warehouse-inspired vibe to your space. Ultimately, the choice of your coffee table aesthetic should reflect your personal style and the overall theme of your home. Whether you lean towards minimalism, embrace rustic charm, go bold and eclectic, opt for luxury, or appreciate the industrial edge, there is a coffee table out there to suit your preferences. This essential piece of furniture not only provides a surface for your coffee and décor but also tells a story about your taste and creativity, making it a crucial element in your home’s interior design.
In contrast, industrial coffee tables have gained popularity for their rugged and utilitarian charm. Made from materials like steel, concrete, and reclaimed wood as coffee table manufacturers, these tables exude a raw, unfinished look. Industrial coffee tables often feature sturdy construction and distinctive features such as wheels, gears, or visible hardware, making them ideal for adding an urban, warehouse-inspired vibe to your space. Ultimately, the choice of your coffee table aesthetic should reflect your personal style and the overall theme of your home. Whether you lean towards minimalism, embrace rustic charm, go bold and eclectic, opt for luxury, or appreciate the industrial edge, there is a coffee table out there to suit your preferences. This essential piece of furniture not only provides a surface for your coffee and décor but also tells a story about your taste and creativity, making it a crucial element in your home’s interior design.
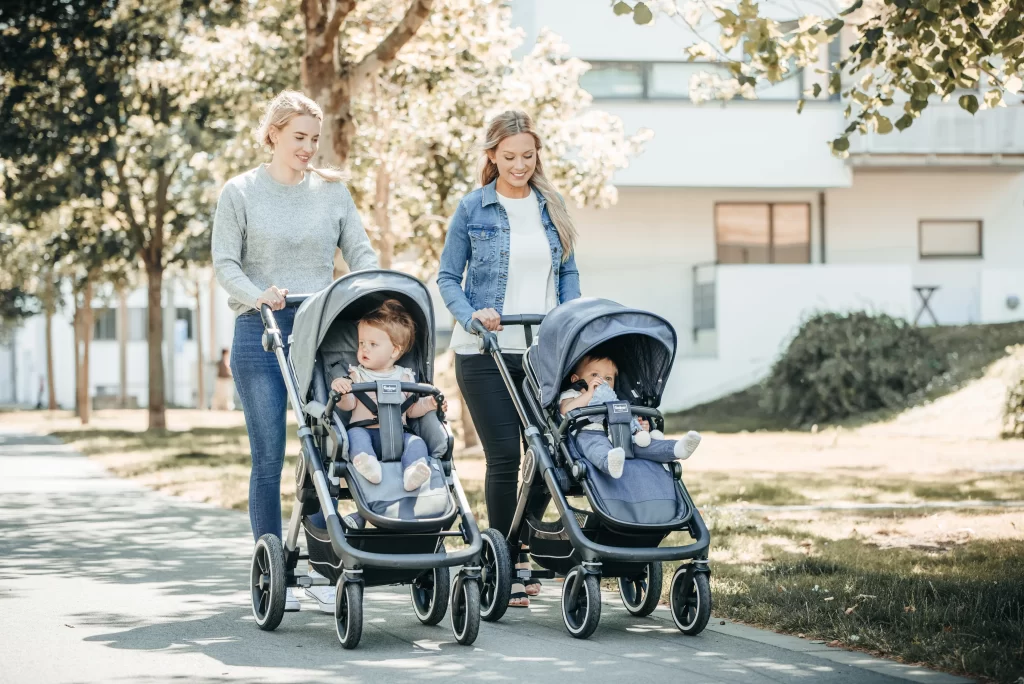 Sleek and chic strollers are not just about looks they also boast innovative features that cater to the needs of both parents and babies. From multi-position reclining seats to one-handed folding mechanisms, these strollers are designed with convenience in mind. One popular feature in modern strollers is the ability to adapt to various terrains. Parents can easily switch from smooth city sidewalks to bumpy park paths with strollers that have advanced suspension systems and robust wheels. This adaptability is a boon for parents who want to maintain an active lifestyle without compromising their baby’s comfort. Moreover, many of these strollers offer adjustable canopies with SPF protection, ensuring that your child is shielded from the sun’s harmful rays, while transparent peek-a-boo windows allow parents to keep an eye on their little one.
Sleek and chic strollers are not just about looks they also boast innovative features that cater to the needs of both parents and babies. From multi-position reclining seats to one-handed folding mechanisms, these strollers are designed with convenience in mind. One popular feature in modern strollers is the ability to adapt to various terrains. Parents can easily switch from smooth city sidewalks to bumpy park paths with strollers that have advanced suspension systems and robust wheels. This adaptability is a boon for parents who want to maintain an active lifestyle without compromising their baby’s comfort. Moreover, many of these strollers offer adjustable canopies with SPF protection, ensuring that your child is shielded from the sun’s harmful rays, while transparent peek-a-boo windows allow parents to keep an eye on their little one.